The name “Dissolved Air Flotation” (DAF for short) is slightly misleading, because it is not actually the dissolved air that causes flotation, but the fact that the air comes out of solution to form bubbles. To understand this, we need to start at the basics.
What is Flotation
Flotation (sometimes spelled floatation) is simply the act of floating in a liquid or gas. In the case of water treatment it refers to the action of floation solids and other contaminants to the surface of the liquid.
The principle of removing contaminants with (air) bubbles is no complicated: small bubbles get released from the bottom of the tank that float up. As they float up, the bubbles remove contaminants in multiple ways:
- Buoyancy: the bubbles physically move particles up as they float upwards;
- Entrapment: smaller particles can get ‘stuck’ on or in the bubbles and float upwards, forming a froth layer;
- Diffusion: dissolved gases can diffuse into bubbles, following the same principle of a distillation column or gas exchange column, and be removed at the top of the tank.
How Does Dissolved Air Change Flotation?
Knowing the principle of flotation, dissolved air flotation becomes easier to understand. The “dissolved” part of DAF refers to the air that is dissolved in an incoming water flow under pressure. Part of the clarified water that flows out of the DAF unit is recirculated back to the bottom of the tank. This flow is pressurised and brought into contact with pressurised air. When the water with dissolved air enters the bottom of the tank, the pressure is instantly reduced as the flow goes through a nozzle. This decompression causes air to come out of solution and form microscopic bubbles, smaller than any nozzle could create if the air was gaseous when it entered.
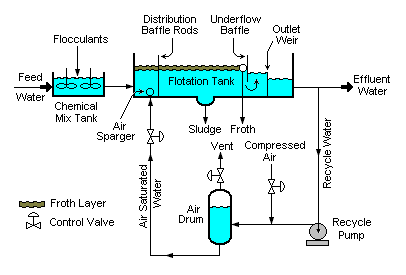
Image credit mbeychok, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
The schematic above shows a standard design of a DAF system. The core system is the flotation tank with the recycle water loop, compressed air injector, air drum, and air saturated water return line. The air sparger is often a porous block of stone or metal, used to rapidly distribute the partially saturated water.
The microscopic air bubbles prefer to form around nucleation points, such as impurities in the water. This could be small particles such as sand or organic matter, or even larger molecules that are dissolved in the water. Since the air molecules cluster around the contaminant as they form a bubble, the contaminant is captured in the bubble more effectively compared to the use of bubbles.

The image on the left shows microfoam floating on top of a DAF filter tank. Note how the foam is very small and does not form larger bubbles. The size of the bubbles can vary based on the contaminants in the water
Image credit Enviplan, CC BY-SA 4.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Uses of Dissolved Air Flotation
DAF is used in many industries in which water (or other liquids) need to be clarified. Traditionally, DAF is used for the removal of oils and fats from wastewater, because the microscopic bubbles are very effective at removing them, down to individual molecules. This use is widespread in the petrochemical industry since they deal with oil removal from water streams a lot, and this is a simple system. In case of flammables, pure nitrogen is used to avoid creating explosive atmospheres.
In wastewater treatment, DAF is sometimes used for this purpose – to remove oils and fats – but it is also used in smaller scale treatment works to remove organic matter.
Conclusion – What is DAF
Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is a water clarification technique widely used in wastewater treatment, especially in the petrochemical industry. Pressurised water with dissolved air is released at the bottom of a tank, and the decompressed air forms microscopic bubbles around particles and contaminants in the water. This causes the contaminants and bubbles to float to the top and form a foam layer which can be removed.
[…] For a more basic overview of dissolved air flotation and its uses, see our basic guide to DAF. […]